Building a Greener Future: Sustainable Architecture Innovations
Sustainable architecture is more than a trend; it’s a fundamental shift towards creating environmentally conscious and energy-efficient structures that contribute to a greener future. Let’s delve into the innovations and principles driving sustainable architecture.
Environmental Consciousness in Design
At the heart of sustainable architecture lies a deep commitment to environmental consciousness. Designers and architects prioritize eco-friendly materials, energy-efficient systems, and green building practices that minimize the environmental footprint of structures. The goal is to create buildings that harmonize with their surroundings and contribute positively to the natural ecosystem.
Innovative Materials for Eco-Friendly Structures
Sustainable architecture embraces a variety of innovative materials with lower environmental impact. From recycled and reclaimed wood to bamboo, which grows rapidly and is highly renewable, architects are exploring materials that reduce dependence on traditional, resource-intensive options. These choices not only promote sustainability but also often result in unique and aesthetically pleasing designs.
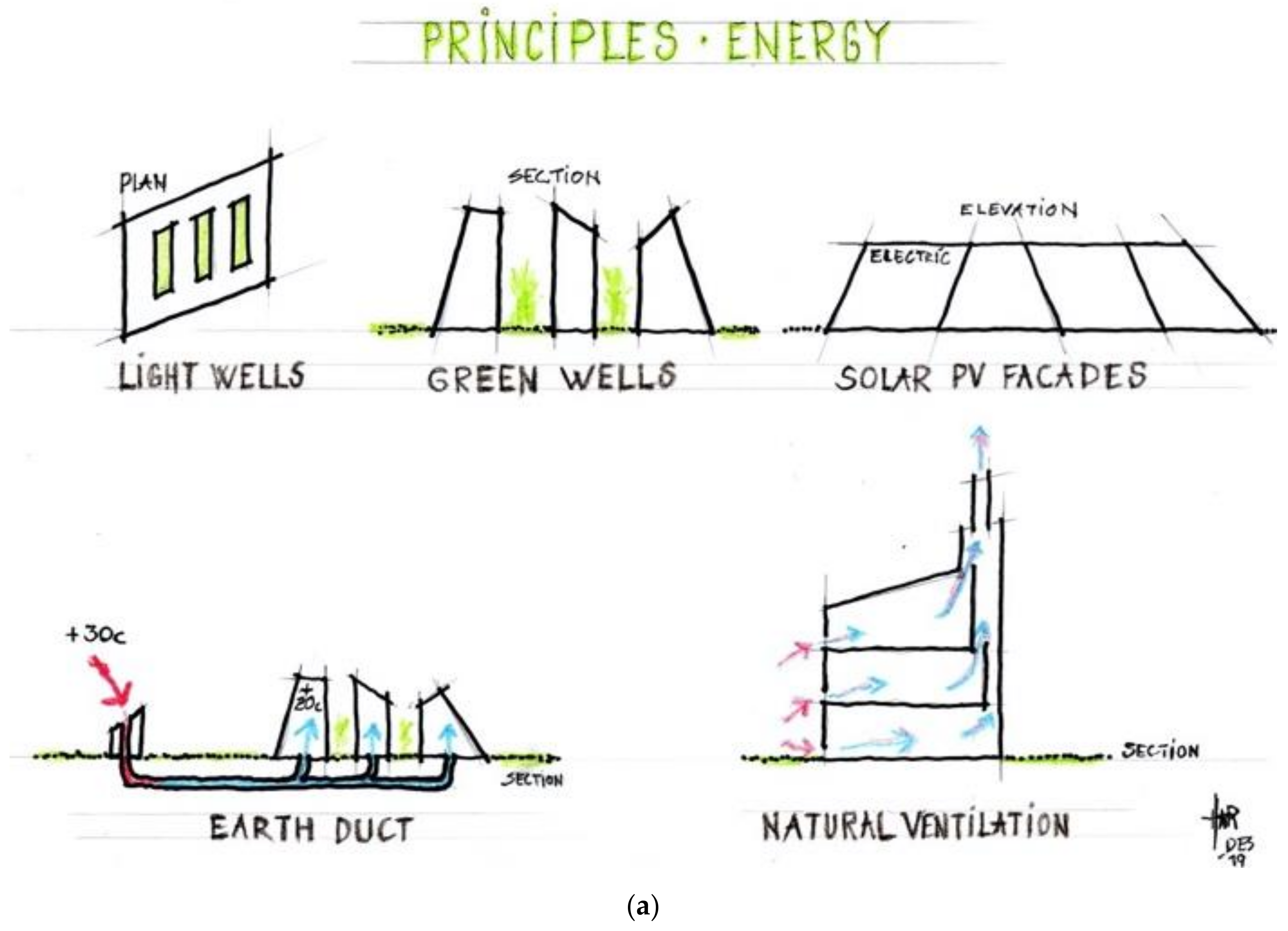
Energy-Efficient Building Systems
One of the key pillars of sustainable architecture is energy efficiency. Buildings are designed to optimize natural light, utilize passive heating and cooling techniques, and incorporate advanced insulation systems. Additionally, renewable energy sources such as solar panels and wind turbines are integrated to generate clean energy, reducing reliance on conventional power grids.
Waste Reduction and Recycling Practices
Sustainable architecture actively addresses the issue of construction waste by implementing efficient waste reduction and recycling practices. This involves repurposing materials from demolition, minimizing excess construction waste, and adopting recycling systems. These practices not only contribute to sustainable building but also set an example for responsible construction methods.
Green Roofing and Vertical Gardens
Green roofs and vertical gardens are becoming prominent features in sustainable architecture. Green roofs involve growing vegetation on building rooftops, providing insulation, reducing heat absorption, and promoting biodiversity. Vertical gardens, on the other hand, not only enhance aesthetics but also improve air quality and contribute to urban biodiversity, showcasing the multifaceted benefits of sustainable design.
Sustainable Architecture: A Link to Greener Living
For those seeking insights into sustainable architecture, Sustainable Architecture offers a wealth of information and inspiration. Explore the latest trends, case studies, and success stories from a community dedicated to building a greener, more sustainable future.
Water Conservation and Efficient Usage
Sustainable architecture places a strong emphasis on water conservation. Design strategies include rainwater harvesting systems, water-efficient fixtures, and landscaping that minimizes water requirements. These measures not only reduce the environmental impact but also contribute to overall water conservation efforts.
Biophilic Design for Human Well-being
Biophilic design is a key component of sustainable architecture, integrating natural elements into the built environment to enhance human well-being. This may involve incorporating natural light, greenery, and natural materials to create spaces that promote physical and mental health. The result is not just environmentally friendly buildings but also spaces that positively impact occupants.
Certifications and Standards for Sustainability
Various certifications and standards guide the implementation of sustainable architecture principles. LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design), BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method), and other regional certifications set benchmarks for sustainable building practices. Compliance with these standards ensures that buildings meet established criteria for environmental performance.
Community Impact and Social Sustainability
Sustainable architecture extends beyond the physical structures to consider the broader community impact. It involves engaging with local communities, creating spaces that foster social interaction, and addressing the needs of diverse populations. Social sustainability is a crucial aspect, ensuring that sustainable architecture benefits not only the environment but also the people who inhabit and interact with these spaces.
Conclusion: Shaping a Sustainable Tomorrow
In conclusion, sustainable architecture is a catalyst for positive change in the construction industry. Through eco-conscious design, innovative materials, energy efficiency, and a holistic approach to environmental and social impact, sustainable architecture is shaping a future where buildings coexist harmoniously with the planet. Explore the link to greener living and be inspired to contribute to a sustainable tomorrow.
